Trigonometry/Phase and Frequency: Difference between revisions
imported>Musical Inquisit Added a section explaining the cosine and sine functions, added a problem set that may be useful for students to understand. |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 06:00, 21 March 2020
Frequency
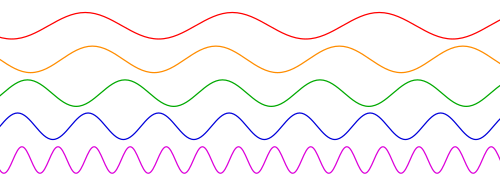
Here are some sinusoidal (that is 'sine like') graphs. These show sinusoidal waves with different frequency. The frequency increases as you go down.
Template:ExerciseRobox In physics, light is a kind of wave, and different frequencies of light give the different colors of the spectrum.
- Does red light have a higher or lower frequency than blue light?
- In a rainbow is red on the outside or the inside of the rainbow? What about a double rainbow? (use the Internet)
- Are radio waves higher or lower frequency than light waves? (use the Internet)
Template:ExerciseRobox In physics sound is a kind of wave. It's physically a different kind of wave from light, but its vibrations can still be described using sines and cosines. Light is an electromagnetic wave and sound is a wave involving change in air pressure. That difference is the underlying reason why light can travel through the vacuum of space, but sound cannot.
High pitched notes are high-frequency sound waves. Low pitched notes are low-frequency sound waves.
- Find out what the highest frequency of hearing is for humans and for bats. (use the Internet)
- Explain in your own words what 'Hertz' means, and what the K in the abbreviation KHz means.
- What vibration frequencies are typical in an Earthquake?
Sine and Cosine Graphs
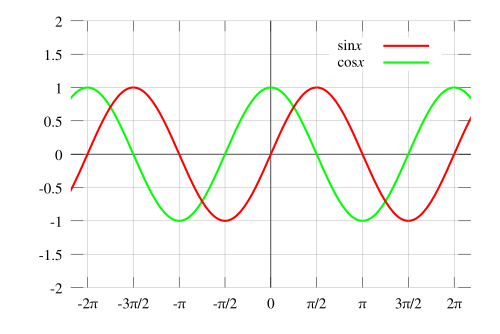
And here in this graph, the colors we've chosen to draw the waves in have no relation to the frequency. Both waves have the same frequency, but we've used different colors.
Notice that in the graph of sine and cosine above that the two graphs have the same shape. If we slide the sine graph slightly to the left, it coincides exactly with the cosine graph. Using the terminology used to describe sinusoidal waves, they have the same amplitude, the same frequency and different phases.
Definitions
A sinusoidal wave is characterized by three parameters: amplitude, frequency and phase.
- The amplitude is the amount the function varies, positively or negatively, from zero in the y direction.
- The frequency is how many complete cycles there are of the wave in unit distance on the x axis (which often measures time)
- The phase is relevant when comparing two waves of the same frequency. It is how much (measured in degrees or radians) one is shifted relative to the other on the x axis.
This terminology comes from sound engineering where higher frequency sounds have higher pitch and waves of greater amplitude are louder.
As an alternative to specifying the frequency, the number of cycles in unit distance, we can instead specify the wavelength, the length of one cycle. The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength. The lower the frequency the longer the wavelength.
You can check this on the diagram of waves of different frequencies at the top of the page.
In More Detail
To fully understand how each of the following definitions relate, look at the graph of the function below (left). For the figure representing (a)-(b), read the corresponding definitions.

Amplitude
The amplitude is the maximum amount that the wave differs from the sinusoidal axis value, – the value by which the function is shifted by the average of the maximum to the minimum range of the function, . The amplitude comes from two different locations: the maximum value minus or the minimum value minus . The positive magnitude of the value is taken (absolute value). Look at the data below for an example.
Let us not worry about finding the function for this set of data for now. Instead, focus on finding the amplitude. The maximum -value . The minimum -value . Therefore, . The maximum difference comes from two different locations: the maximum value minus the sinusoidal axis value or the minimum value minus the sinusoidal axis value. In this example, we will choose to use the difference between the maximum value to the sinusoidal axis value, which is . Therefore, the amplitude of the above data is .
In general, for and (where ) the amplitude is 1. For and (where and ) the amplitude is . The difference between the greatest and least value is called the double amplitude or peak to peak amplitude. Knowing this, the way to find the amplitude given the greatest and least value of the range is to take the difference between the two and then divide by 2:
- .
Frequency
The frequency (sometimes ) is the number of cycles a wave goes through in a standard distance or time. If this standard distance is or radians, the frequency of and is , and that of and is . A graph of a high frequency wave shows more complete cycles in the same horizontal span as a low frequency wave. Notice is the frequency value, , so .
The wavelength (or period), , decreases as the frequency increases. Mathematically, this relationship is written as (the wavelength is inversely proportional to the frequency). It is the distance over which a complete cycle occurs, that is, the wave goes from to its maximum positive value, back to , down to the lowest negative value, then back up to .
The functions and both go through a complete cycle as the angle increases by or radians, hence this is the wavelength. The functions and (where is any positive number) go through one cycle as the angle increases by or , hence their wavelength or . This makes sense, because if and , then .
Finally, using wavelength, one can directly find the frequency. If , then
Phase Shift
The phase is the fraction of the cycle that you have reached at any given point. If the point is not specified, it may be assumed to be 0°. The start of the cycle is the point where the wave is 0 and going from negative to positive. (If the wave is not a sine curve, there may be more than one such point in a complete cycle so the starting point may be arbitrary.) For the phase at 0° is 0; for it is ¼. If the cycle has wavelength or radians, the phase is often expressed as an angle corresponding to the given fraction of the wavelength, so the phase of at 0° is or radians.
It is assumed that the average value of the wave is 0. If the wave is say or , it is never 0 so to define the phase we would need the point where it reaches its average value (4 in this case).
Examples
has ten times the amplitude of
The graph oscillates between 10 and -10 on the y axis. Template:Robox/Close
has a higher frequency than
There will be 100 times as many cycles in the same distance along the x axis. The amplitude is unchanged.
The wavelength is also decreased. The distance along the x axis for a complete cycle is one hundredth of what it was before. Template:Robox/Close
has a different phase from . The phase difference happens to be 90°, because . If two waves are 180° out of phase then where one is positive the other has the same value only negative. is 180° out of phase with Template:Robox/Close
Offset
Two sinusoidal waves may also have a different offset to each other, i.e. their average values are different, but they still have the same shape. Their graphs are y shifted relative to each other. In sound engineering this is called DC Bias.
has a different offset to . Whereas takes both positive and negative values, is never below 0. Template:Robox/Close
This offset is based off the vertical shift, also known as the sinusoidal axis value. Keep in mind, unlike other functions, this vertical shift does not denote the y-intercept. The only way to determine the y-intercept correctly is to substitute zero into a function. Quick quiz: what is ? In case you forgot, it is . Therefore, the y-intercept for is .
The Graphs and Their Differences
Comparing and contrasting two different items may seem like a pointless task to the student, at first. However, the purpose of such an activity is to make students analyze information and help cement differences between the two ideas. Here, it is imperative that the student understands the differences between cosine and sine because otherwise, the student is not able to model situations correctly! While this Wikibooks will not make the student analyze the two functions themselves, it may be a good idea to remember the differences.
The parent functions

The sine and cosine functions are shown above, where . Notice that the frequency and period of the functions are both identical. Given that these are also parent functions, the vertical shift is zero. However, the similarities start to end. First, look at the pattern of the function. Over , the periodic function follows the basic pattern of "middle," "top," "middle," "bottom," "middle." That is, the value of starts at . However, . This is the highest possible value of sine when looking at the positive values, because the unit circle is peaked when . At , . This has again to do with the unit circle. If you remembered the patterns you identified in the circle (or even the unit circle itself) you can infer howwill look like. The minimum value of the range is at precisely for this reason. As such, the pattern we identified is always true.
By contrast, the cosine function follows a more simplistic pattern. For , you already start at the maximum value because is the largest -value on the circle, while is the lowest -value on the circle. Because of the unit circle, the simplistic pattern results: "maximum," "medium," "minimum," "medium," "maximum."
The patterns mentioned above are things that you should keep in the back of your mind. These patterns are the main ways in which a person can easily identify when to use one particular function over another. When a phase shift is applied, choosing to use a cosine function or a sine function is best left to student judgement.
From the information we have so far, we get the following information:
- The vertical shift .
- The amplitude .
- The frequency .
The general form of the sinusoidal function is
- The sine can be substituted for cosine and it would work just the same.
- is the amplitude.
- is the frequency.
- is the vertical shift (sinusoidal axis value).
- is the phase (horizontal) shift.
We have described the general pattern for the cosine and sine functions. However, it is important to step back and appreciate the underlying math for which the cosine and sine curves rely on, the unit circle. While these functions are beautiful, the underlying math behind why these functions behave the way they do is the reason for this beauty, and in a way, makes it more beautiful than the end result.

Draw two circles with radii and centered at the origin, where . If a line extending from the origin reaches an endpoint of each circle at the angle , then , and . As such,
Because is multiplied directly to or , for , .
Let , , and . Because we know how to graph , is multiplied directly to , and , the resulting function must be "expanded" over the -axis. This expansion must be related to the amplitude of the function, because and gives . (Recall ).
- The amplitude of the function is given by the radius of the circle.
- Changing the radius of the circle does not change the frequency, the vertical shift, or the phase shift. (Exercise: show that this is true for at least the frequency and the vertical shift.)
This result will be useful when working with problems later.
As of now, increasing the radius is all that we could connect these sinusoidal functions to the circle. We need to understand more about additions and such before one can address the beauty of this math. Nevertheless, always keep this result locked in your heart.
Modeling Situations
The sinusoidal functions are very useful in real life applications, where these periodic (repeating) functions model situations that follow a pattern over a set amount of time, such as in modeling day length, planetary motion, sound waves, energy waves, etcetera.
- Marine biologists determined the average length of fish in a pond in millimeters (mm) is dependent on the time, in years. The table is shown below, where is the time, in years, and is the average length of the fish, in millimeters. Find the sinusoidal function that best models the information provided.
- The situation is given to be periodic and sinusoidal. Therefore, it is best to use the sinusoidal function and its properties: .
- Find the vertical shift, . Recall that . According to the table, the maximum y-value is 44, while the minimum value is 36. Therefore, the vertical shift is
- Find the amplitude, . Recall that . According to the table, the maximum y-value is 44, while the minimum value is 36. Therefore, the amplitude is
- Find the frequency, . Recall that . If the wavelength is the distance whereby a complete cycle occurs, then from to , the cycle is complete. As such, . Given this information,
- For now, let us ignore the phase shift, . Substitute the information we already know into the function above: . Recall that a sinusoidal function that has a maximum value reappear again over a wavelength (from maximum to medium to minimum to medium to maximum) is cosine. As such models the situation sufficiently.
- Equivalently, assuming we want to keep it in terms of sine, we know the following is true:
- Therefore, .Template:Robox/Close
The above question is comparatively easier to other similar problems like this. In the real world, you are less likely to see a steady increase/decrease in fish length because of two factors:
- Evolution: bigger fish are usually seen as predators, which are often avoided. Smaller fish are more likely to be seen as weaker.
- Internal Competition: size among females may be seen as more desirable as mates, and therefore more likely to pass on offspring with those traits. As such, competition may exist among females for desirable mates.
There are many questions a person may be asking: where is the above circle in the question? Why use radians as opposed to degrees? . There are a few reasons, but it requires us to delve more deeply into mathematics that is usually considered advanced (polar coordinates). Unfortunately, Book 1 will not delve into this topic. However, for those that are curious, Book 3 will have polar coordinates that fully explain this behavior.