A-level Computing/AQA/Paper 1/Fundamentals of data representation/Bitmapped graphics
Overview


Resolution

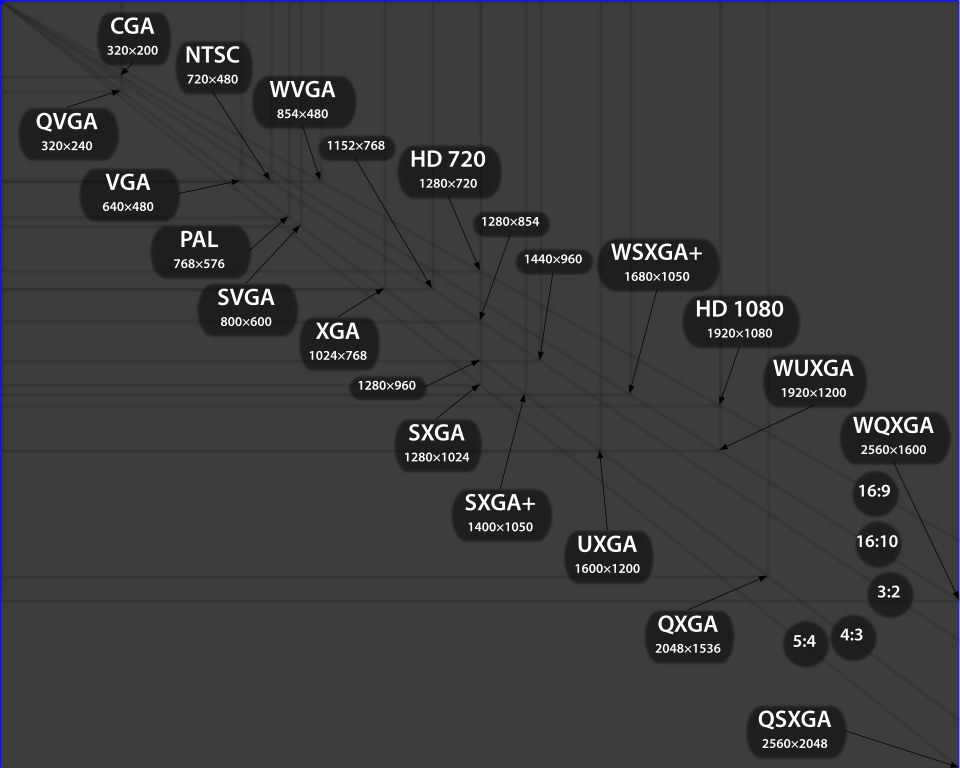
Example
Template:ExampleRobox Using the diagram above we are going to work out how many pixels are required to display a single frame on a VGA screen.
Checking the resolution:
Height = 480 Width = 640 Area = Width * Height = Total Pixels Area = 640 * 480 = 307200
Questions
Template:CPTExercise Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTabThe smallest possible addressable area defined by a solid colour, represented as binary, in an image. Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTabThe amount of pixels an image contains per inch/cm Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTabthe number of pixels per row by the number of pixels per column Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTab100 * 70 = 7000 pixels Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTab30 * 40 = 1200 pixels Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTab1920 x 1080 = 2073600 pixels Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTab700 / 35 = 20 pixels Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTab higher resolution images are able to display more detail, providing crisper images Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:CPTQuestion Template:CPTAnswerTabIt will require a lot of space to store it. Meaning you'll quickly run out of memory, or it'll take a long time to transmit images across the internet or other data route.Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd Template:Robox/Close
Colour Depth
| Colour depth | 1 bit | 2 bit | 4 bit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example |  |
 |

|
| Description | Mono-chrome, only stores black and white | stores 4 colours: RGB(70,61,55), RGB(79,146,85) RGB(129,111,134), RGB(149,146,166) |
Stores limited colours |
| Number of colours per pixel |
|||
| Colour depth | 8 bit | 24 bit | |
| Example |  |

| |
| Description | close to reality | hard to see any difference between reality | |
| Number of colours per pixel |
It seems pretty obvious that the higher the colour depth, the closer the picture will look to reality. Why then don't we just ramp up the colour depth on every image that we make? The answer should be obvious, for a fixed resolution, the higher the colour depth, the larger the file size.
Example
Template:ExampleRobox All the images above are of the same resolution:
300*225 = 67500 pixels
If the first image uses 1 bit to store the colour for each pixel, then the image size would be:
Number of Pixels * Colour Depth = Image Size
67500 * 1 bit = 67500 bits
For the second image uses 2 bits to store the colour for each pixel, then the image size would be:
Number of Pixels * Colour Depth = Image Size
67500 * 2 bit = 135000 bits
| See the rest of the calculations: | ||
|
For the third image using 4 bits to store the colour for each pixel, then the image size would be: Number of Pixels * Colour Depth = Image Size
67500 * 4 bit = 270 000 bits
For the third image using 8 bits to store the colour for each pixel, then the image size would be: Number of Pixels * Colour Depth = Image Size
67500 * 8 bit = 540 000 bits
For the third image using 24 bits to store the colour for each pixel, then the image size would be: Number of Pixels * Colour Depth = Image Size
67500 * 24 bit = 1 620 000 bits
|
||
Questions
Template:CPTExercise
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab The number of bits used to represent the colour of a single pixel
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab 6 as:
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab 8 colours is 3 bits per pixel as:
h * w * b = 20 * 30 * 3 = 1800 bits
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:CPTQuestion
Template:CPTAnswerTab When you want to save file space or when you only need a specific palate of colours such a mono-chrome
Template:CPTAnswerTabEnd
Template:Robox/Close
Template:BookCat