Biological Physics/Boyle's Law
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
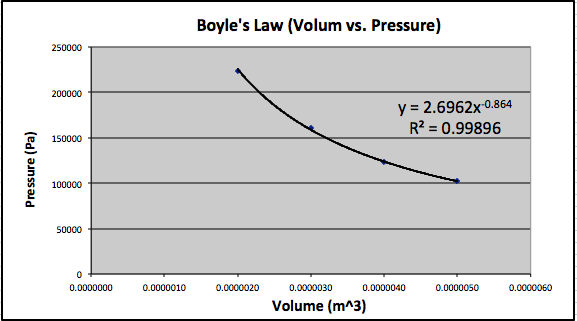
Boyle's Law states that the volume and pressure are inversely proportional. This means that as the volume of gas in a container decreases, the pressure increases. To test Boyle's Law a syringe was attached to a pressure meter and weights were added to the plunger to show the relationship between the volume and pressure inside the syringe. Below is a table of values showing the results of the experiment. In the table to work done is calculated based on the difiniton of work, W=mgΔx, and work derived from the ideal gas law, .
| Mass (kg) | W=mgΔx | Pressure (Pa) | Volume () | Distance (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | ||
| 0.3000 | 0.0265 | 0.1139 | 0.0090 | ||
| 0.8000 | 0.0706 | 0.1468 | 0.0180 | ||
| 1.5000 | 0.1323 | 0.2070 | 0.0270 |
Below is a graph showing the relationship between the pressure and volume inside the syringe.