Calculus/Trigonometry
Template:Calculus/Top Nav Trigonometric functions play an important role in calculus. In many aspects, the trigonometry content here will be fundamental in understanding certain operations in calculus and proofs. The following information below is a review rather than an intended lesson. For more information about trigonometry, please read Trigonometry Book 1.
Measuring angles

In everyday life it is common to measure angles in degrees, where there are 360 degrees in a circle. In mathematics it is often convenient to use a different measure of angles, the radian. There are radians in a circle. Why is the radian used in math? It turns out that the radian is a natural measure of circles. Consider the circle in the figure to the right. is the radius, is an angle with vertex at the center of the circle, and is the arc of the circle subtended by the angle. By using radians as the measure for the equation holds. Certain operations we will study in calculus are simplified by using radians as the measure of angles.
is the unit for radians. However, often times it can be ignored.
Suppose you want to convert between radians and degrees. There are 180 degrees and radians in a half circle. Using the ratio of degrees to radians or radians to degrees in a half circle gives us a scaling factor to convert from radians to degrees or degrees to radians, respectively.
An example calculation below is used to find the measure of
. Notice that
is eliminated when multiplying the two dimensions.
An example calculation is used to find the measure of
. Notice that
and is eliminated when multiplying the two dimensions.
The general formula for converting between radians and degrees is shown below.
In this book, radians will be used much more often than degrees, so it is important to be familiar with the conversion.
Basic trigonometric functions
Functions
The basic trigonometric functions are the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. In mathematical expressions, these are represented as , and respectively. These functions relate the angles in a right triangle to various ratios of the lengths of the triangle's sides. You may recall the mnemonic SOH-CAH-TOA, which helps the student remember these relationships. is the angle of interest, is the length of the side of the triangle opposite the angle, is the length of the side of the triangle adjacent to the angle, and is the length of the hypotenuse. The mnemonic tells us that

,
, and
The other three basic functions are the cosecant, secant, and cotangent functions, which are the reciprocals of the sine, cosine, and tangent functions respectively. The graphs of those functions are on the right.
,
, and
However, such definitions limit the domains of the functions. Because the angles in right triangles can only be
maximum, angles larger than that cannot be defined. So, to solve this problem, the unit circle helps expand the inputs of the function from
to all real numbers. (The unit circle is explained right below this section)
The properties of the functions are summarized below.
| Function | Domain | Range | Parity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sine (sin) | Odd | ||
| Cosine (cos) | Even | ||
| Tangent (tan) | Odd | ||
| Cosecant (csc) | Odd | ||
| Secant (sec) | Even | ||
| Cotangent (cot) | Odd |
Basic values
There are some important values to be memorized in trigonometric functions because these values are a starting point to branch out towards more values. The table below summarizes the basic values of trigonometric functions.
Template:Center/top Template:Center/end Other values of these functions can be calculated through trigonometric identities (see below) and the Taylor series (see Template:Calculus/map page).
The unit circle

A circle with the equation is called a unit circle. Imagine a circle with center at the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system.
Rotating a ray from the direction of the positive half of the x-axis by an angle (counterclockwise for and clockwise for ) yields intersection points of this ray with the unit Template:Nowrap and, by extending the ray to a line if necessary, with the Template:Nowrap and with the Template:Nowrap The tangent line to the unit circle in point Template:Math, which is orthogonal to this ray, intersects the y- and x-axis at points and . The coordinate values of these points give all the existing values of the trigonometric functions for arbitrary real values of in the following manner:
| Function | Right-triangle definition | Unit circle definition |
|---|---|---|
| Template:Sfrac | ||
| Template:Sfrac | ||
| Template:Sfrac | ||
| Template:Sfrac | ||
| Template:Sfrac | ||
| Template:Sfrac |
The importance of the unit circle is that it expands the definitions of trigonometric functions. Before, those values are constrained within a right triangle. Now, the functions can be used on any radian as their input.
Trigonometric identities
The identities listed here are considered as basics for calculus and it is highly recommended for readers to recognize and memorize these identities. For more advanced identities, please go to List of trigonometric identities.
The Pythagorean identity
Right-triangle definition derivation
From the definitions of
,
, and
, one can see that
Likewise,
We can derive some useful identities using the definitions of the trigonometric functions together with the Pythagorean theorem. Recall that, given a right triangle having sides of length
and
and hypotenuse of length
, that
. Suppose the angle opposite the leg length
and the adjacent leg length
is
. By doing some manipulation, we can derive the Pythagorean identity of trigonometry.
Therefore,
There are some transformations of the Pythagorean identity. One way to transform it is to divide the above equation by
Therefore,
Equally, one may multiply the equation by
,
After some adjustments, we get
Unit circle definition derivation
According to the unit circle, assume that there is a point
, the definition tells us that
And since the unit circle has a radius of 1, the distance between point
and the center should be 1. Using the distance formula, we can get
The other versions of the Pythagorean identities in the right-triangle definition derivation can be expanded to the unit circle using the same method. Again, with the help of the unit circle, trigonometric functions are not limited within the triangle. It expands the perspective of those functions from triangles to all real angles.
This identity is important in later chapters when we discuss trigonometric substitution (see Chapter Template:Calculus/map page).
Identities of angle addition and subtraction
There are more values to the domain of the trigonometric functions than , , , and its multiples. There are infinitely many inputs possible for the sine and cosine functions. Techniques were found along the way to calculate the exact values of some "untraditional" values for . Take a look at the example below:
The exact value can, with confidence, be declared absolutely correct because there is a formula for sine that can evaluate .
This is the angle addition formula for sine.
The formulae for other functions are listed below:Template:Calculus/Def
Proof for addition
This proof uses a great deal of geometry. However, there is another way to prove this using Euler's formula, which is currently beyond our knowledge.
Look at the image on the right, which consists of 4 right triangles: the blue triangle, the red triangle (with a hypotenuse of 1), the upper-left triangle, and the upper-right triangle. According to the definition of trigonometric functions, the adjacent and opposite sides (respective to the notated angles) should be:

Red opposite Blue opposite Upper-left opposite Upper-right opposite Red adjacent Blue adjacent Upper-left adjacent Upper-right adjacent
Now, let's broaden our view from the individual triangles to the rectangle as a whole. Since opposite sides of a rectangle should have the same length, the following equations should be true.
Upper-left opposite
Blue opposite
Upper-right adjacent
Upper-left adjacent
Blue adjacent
Upper-right opposite
Then, plugging in the values will yield:
Simply dividing the equations above will yield the tangent formula.
Proof for subtraction
Subtraction is just a special case of addition: . Thus, using this clever manipulation, one can save a lot of time from drawing triangles.
Actually, before starting the calculation, let us review the properties of trigonometric functions (you can find it right above this section). Since the sine function is an odd function, it has the following identity. (for the definition of odd and even functions, see Chapter Template:Calculus/map page)
Since the cosine function is an even function, the following equation is also true.
Thus,
So, the case of calculating
is now solvable. Using what we have just derived, we can get:
For the other three trigonometric functions (cosecant, secant, and cotangent), one can apply the definition of these functions and do some adjustments.
These additional formulae are not required to be memorized because knowing the first three formulae (sine, cosine, and tangent) is sufficient to deduce the other three.
Applications
In certain countries, students are required to memorize the specific examples of the applications of the formulae. Those specific examples are called the induction formulae because those examples are widely used in scientific problems and would save a lot of time substituting the values into the original formulae.
However, there is a better way to understand the induction formulae with the help of the unit circle.
For example, the periods of even numbers of can be interpreted as rotating the angle on the unit circle for full revolutions, while the periods of odd numbers of can be interpreted as rotating the angle on the unit circle for half a revolution and then full revolutions. Those transformations can be plotted on the unit circle, which makes the process convenient for people to calculate.
Shifts of even numbers of Shifts of odd numbers of Parity (symmetry about the x-axis in the unit circle) Symmetry about the y-axis in the unit circle transformations of
There are many more examples and applications by using this identity. The table above only lists selected groups of examples. It would be great if you can plug in specific numbers into the formulae and do some experiments.
Double-angle formulae
It is highly recommended that readers should memorize and be familiar with the processes because of the convenience they will provide.Template:Calculus/Def
Proof
The double-angle formulae are easy to derive by using the addition identities of trigonometric functions. The reason that the formulae are separated from the applications of the addition and subtraction identities is that the double-angle formulae also serve as a base for the half-angle formulae and a way to transform between powers. Those formulae will be very useful in calculus, especially when one needs to lower the power of the exponents.
In the
case, we can use the Pythagorean identity to transform the formula to other forms.
Thus, the double-angle formulae are complete.
Half-angle formulae
The half-angle formulae can be interpreted as the reverse of the double-angle formulae. The proof is not difficult. Using what we already know, we can derive the formulae quite easily. Template:Calculus/Def First, we understand that:
There are only two equations that are important for the derivation.
and
Now, let . So:
and
After some adjustments, one can get:
and
However, this can be improved because the exponents on the left side of the equations are not eliminated. The problem is that one cannot simply take the square root of the whole equation because the positive and negative signs matter a lot. So, in order to solve the problem, a function is used.
Therefore, the formulae can be improved.
It is recommended that it would be more convenient to simply use the unit circle to determine the signs of the answers. Furthermore, the equations with exponents are more frequently used in calculus because the reason that the half-angle formulae make integrating more convenient is that the formulae can eliminate exponents rather than create square roots.
Tangent half-angle substitution
The tangent half-angle substitution is very powerful because any basic trigonometric function can be written in terms of . Template:Calculus/Def
Proof
The proof is slightly difficult because it requires special manipulations regarding the double-angle formulae. Let us start with the sine function first. We already know that . Let us do some adjustments. First, write the equation into a fraction.
Now, divide both the nominator and the denominator by
After some cancellations and adjustments, and knowing that :
Since the Pythagorean identity states that :
In the end,
The derivation for cosine is also similar
(the double-angle formula) (divide both sides by ) (do some adjustments) (use the Pythagorean identity)
There is basically no derivation for the tangent formula because it is the same as the double-angle formula for tangent:
Law of sines and cosines
These laws are more of an application of trigonometry than identities, but they are equally important compared to their counterparts. Template:Calculus/Def
Proof

The proof for law of sines involves the formula for the area of a triangle, which is:
In the triangle portrayed on the right, there are three ways to describe the area, which are:
Then multiply these by .
The proof for law of cosines involves the Pythagorean theorem, which is:
(when triangle
is a right triangle with
as its hypotenuse)
In any triangle, the Pythagorean theorem can be written like this.
Since according to the Pythagorean identity of trigonometry
More identities will be discovered as we wander deeper into the world of Calculus.
Inverse trigonometric functions
The inverse trigonometric functions are, as the name suggests, inverse functions of trigonometric functions. Since inverse functions are defined as:
the concept of inverse trigonometric functions are not hard to digest.
There are two common versions of notations for inverse trigonometric functions. One is intuitive because of the definition: the inverse function of is . However, because this may be mistaken as the reciprocal of the function very easily, this section and hopefully this book will use the second notation:
Properties
The inverse functions are basically a process of reversing the original functions. For example, if is the inverse function of and , then . The process of transforming to is reversed so that the process is now from to . Such identity also exists in inverse trigonometric functions. Instead of turning an angle into a linear length, inverse trigonometric functions turn linear lengths into angles.
- , so .
However, as a function, they still need to obey basic rules of functions, which is: By definition, for each "input" a function returns only one "output", corresponding to that input. While the same output may correspond to more than one input, one input cannot correspond to more than one output. (see Template:Calculus/map page). In other words, there can only be one result. Since many angles can have the same result in trigonometric functions, the so-called inverse trigonometric functions are technically not functions. Take the following for example:
- (not a function)
So in order to solve the multiple outputs problem, mathematicians limit the domain and range of those so-called inverse trigonometric functions so that situations like the one above can be avoided. And since there are no multiple outputs after the limitation, those so-called inverse trigonometric functions are finally functions.
| Function | Domain | Range | Graph |
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
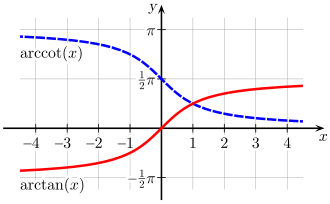 | |||
 | |||
Note that the ranges for arccosecant and arcsecant may vary among different texts.
General Solutions
Because those inverse functions are considered as functions, the output of those functions are not the general solutions for problems like this:
Find all angles that satisfy
Since
, the answer should be
. However, after checking the answer on the unit circle, we can find that
also satisfies the question. So, there should be a way of using the function arcsine to represent all the possible angles that fulfill the requirement. Fortunately, there is. One way to write the answer is:
As one can see,
and
. Substituting those results into the answer will yield:
Now, by substituting
as
, the general solution for
is:
Using the same way, the general solutions for other equations are:
| Question | Solution |
|---|---|
Other questions such as can be simplified as .
Since inverse functions have the identity of , . Thus, when handling equations like this: , where is a constant, the general solution can be more simplified because .
Relations
The following table demonstrates the relationships between trigonometric functions and inverse trigonometric functions.
It is not difficult to prove these. Take
for example. First, let
. So
Since
and
,
Since
,
Thus,
.
Other relationships can be proved through this method.
Related functions
These other related functions though serve as an equally important role in calculus, it is not required to be memorized as intensely as the basic ones on the top page.
Hyperbolic functions

Hyperbolic functions is an alternative form of trigonometric functions. While trigonometric functions are defined on the unit circle (see section on top), hyperbolic functions are defined on the positive x-axis of the unit hyperbola (see more on Hyperbolic functions).
The unit hyperbola has the equation
. Since hyperbolic functions are only defined on the positive x-axis part of the equation, more specifically, we just want this part of the equation:
Rotating a ray from the direction of the positive half of the x-axis by an angle
(counterclockwise for
and clockwise for
) yields intersection points of this ray with the unit hyperbola:
. It is defined that:
where
is twice the area between the ray, the hyperbola, and the
-axis.
According to the definition, we can see that .

Euler's formula
Euler's formula is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that for any real number x:
For those who don't know,
is the natural base of the logarithm and
is the imaginary unit
. This formula is extremely useful in a variety of scientific fields. However, this is not within the scope of this particular chapter. This formula will be mentioned in Chapter Template:Calculus/map page.Template:Calculus/Top Nav